パターンについて
オブジェクトをラップし、別のインタフェースを提供します。
※ アダプタ、デコレータ、ファサードパターンの違い
アダプタは、オブジェクトのインタフェースを変更するためにラップします。
デコレータは、新しい振舞いや責務を追加するためにラップします
ファサードは、簡素化のために一連オブジェクトを「ラップ」します
HeadFirstデザインパターンでの定義
クラスのインタフェースをクライアントが期待する別のインタフェースに変換します。
アダプタは、互換性のないインタフェースのためにそのままでは連携できないクラスを連携させまます。
パターン構造
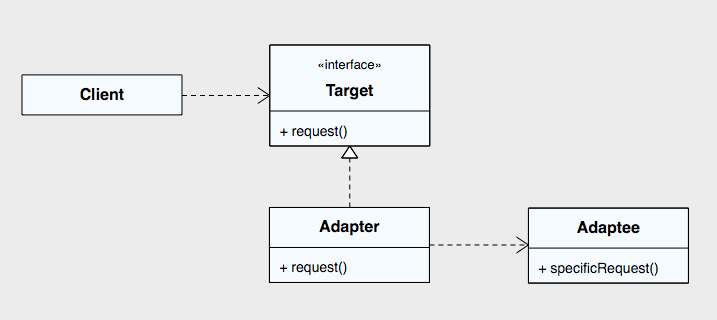
構成要素
Client : Tragetインタフェースを利用する処理
Target : 変換時に実装したいインタフェース
Adapter : TargetクラスのインタフェースをAdapteeクラスの処理利用して実装します
Adaptee : インタフェースの変換を行う元クラス
サンプル
真鴨クラスを七面鳥クラスとして扱いたい場合
・鴨
1 2 3 4
| public interface Duck { public void quack(); public void fly(); }
|
・真鴨(Adapee)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| public class MallardDuck implements Duck { public void quack() { System.out.println("Quack"); } public void fly() { System.out.println("I'm flying"); } }
|
・七面鳥(Target)
1 2 3 4
| public interface Turkey { public void gobble(); public void fly(); }
|
・Adapterクラス(Adapter)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
| public class DuckAdapter implements Turkey { Duck duck; Random rand; public DuckAdapter(Duck duck) { this.duck = duck; rand = new Random(); } public void gobble() { duck.quack(); } public void fly() { if (rand.nextInt(5) == 0) { duck.fly(); } } }
|
・実行コード(Client)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
| public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { MallardDuck duck = new MallardDuck(); Turkey duckAdapter = new DuckAdapter(duck); for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { System.out.println("The DuckAdapter says..."); duckAdapter.gobble(); duckAdapter.fly(); } } }
|

